Cemented carbide, also known as hard alloy, is a composite material made by combining a hard phase (typically tungsten carbide, WC) with a metallic binder (usually cobalt or nickel) through a sintering process. Its exceptional properties—such as high hardness, wear resistance, strength, and thermal stability—make it a critical material in the manufacturing of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) parts, particularly in precision machining and tooling applications.
1. Key Properties Relevant to CNC Applications
- High Hardness: Cemented carbide maintains hardness levels close to that of diamond (typically 85-93 HRA), enabling it to cut, grind, or shape tough materials like steel, titanium, and composites.
- Wear Resistance: Its resistance to abrasion ensures longevity and consistency in high-speed machining processes, reducing tool replacement frequency.
- Thermal Stability: It can withstand elevated temperatures (up to 800-1000°C) generated during CNC operations without deforming or losing cutting efficiency.
- Toughness: The metallic binder provides sufficient toughness to prevent brittle fracture under mechanical stress.
2. Applications in CNC Parts
Cemented carbide is predominantly used in the following CNC components and processes:
- Cutting Tools:
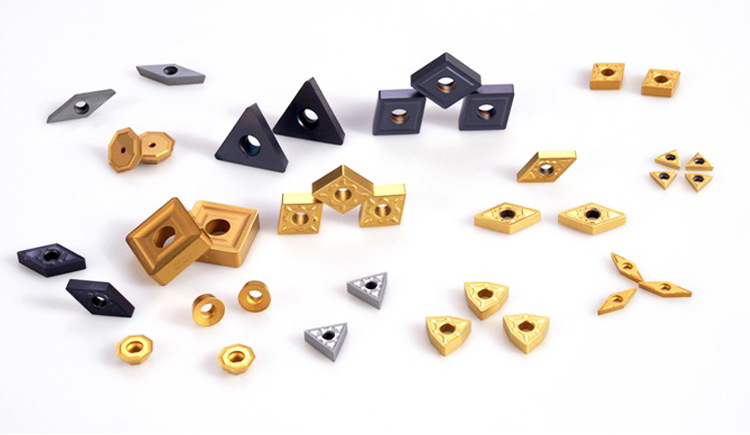
- End Mills, Drills, and Inserts: Cemented carbide is widely used to fabricate cutting tools for milling, drilling, and turning operations. For example, carbide-tipped end mills are preferred for machining hard metals and alloys due to their durability and precision.
- Coated Carbide Tools: Often coated with materials like TiN (Titanium Nitride) or AlTiN (Aluminum Titanium Nitride), these tools further enhance wear resistance and reduce friction during CNC machining.
- Tool Holders and Inserts: Replaceable carbide inserts are used in CNC lathes and milling machines, allowing for quick tool changes and consistent performance in mass production.
- Wear Parts: Components such as guide bushings, nozzles, and dies in CNC setups benefit from carbide’s wear resistance, especially in abrasive environments.

3. Advantages in CNC Machining
- Precision and Surface Finish: The material’s rigidity and sharpness enable tight tolerances and superior surface finishes, critical for aerospace, automotive, and medical parts.
- Efficiency: High cutting speeds and feeds are achievable, reducing machining time and increasing throughput.
- Versatility: Cemented carbide tools can handle a wide range of workpiece materials, from soft aluminum to hardened steels, making them indispensable in diverse CNC applications.
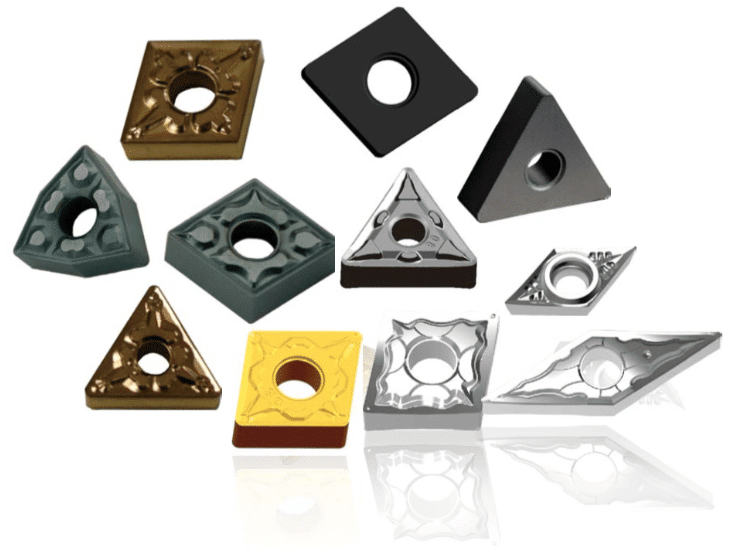
4. Limitations
- Cost: Cemented carbide tools are more expensive than high-speed steel (HSS) alternatives, though their longevity often justifies the investment.
- Brittleness: Despite the binder, carbide can chip or fracture under excessive vibration or improper machining parameters, requiring careful CNC programming.
- Recycling Challenges: While recyclable, the process of reclaiming tungsten and cobalt is energy-intensive.
5. Trends and Innovations
- Micro-Grain Carbide: Finer grain sizes improve toughness and edge sharpness, ideal for micro-machining in electronics and medical industries.
- Advanced Coatings: Developments in PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) and CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) coatings enhance tool life and performance.
- Sustainability: Efforts are underway to improve the recyclability of carbide tools, aligning with eco-friendly manufacturing practices.

Conclusion
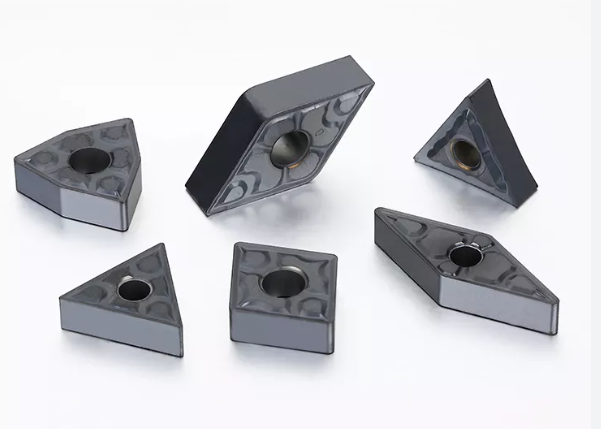
Cemented carbide plays an indispensable role in CNC machining due to its unmatched combination of hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability. Its application in cutting tools, inserts, and wear parts enhances precision, efficiency, and durability in the production of complex parts across industries. While cost and brittleness pose challenges, ongoing advancements in carbide technology continue to solidify its position as a cornerstone material in modern CNC manufacturing.
Tungsten carbide wear parts and cutting tools are critical components in the modern manufacturing industry, prized for their exceptional mechanical properties, extreme hardness, and ability to maintain high performance even under high-temperature conditions during demanding machining operations.
In the production of these precision tools, computer-aided design (CAD) is first used to create detailed 3D models, which are then translated into toolpaths using computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software. These programs are executed on advanced CNC mills and CNC lathes, where optimized feed rates, spindle speeds, and depth of cut allow efficient material removal from tough substrates such as stainless steel and other high-strength alloys.
The primary machining processes employed include milling and turning, along with precision grinding and EDM (electrical discharge machining) to achieve the final geometry and razor-sharp cutting edges. While injection molding with binder-rich grades is sometimes used for near-net-shape forming of complex wear parts (followed by sintering), the majority of high-precision cutting tools still rely heavily on CNC processes and diamond-wheel grinding to meet the exacting tolerances required in today’s high-performance manufacturing environments.
“Zhuzhou Old Craftsman Precision Alloy Co., Ltd. over 18 years of experience in the industry, we specialize in providing customized tungsten carbide wear solutions to meet the demanding requirements of industries such as aerospace, automotive, mining, and precision machining.”
Belt scraper Brazing brazingprocess CARBDIE HAMMER carbide Carbide belt scraper carbidebrazing carbide hammer Crusher CRUSHER HAMMER Informational Internal stress metal mining Refractory Brick Mold Secondary belt cleaner scraper stresses VSI crusher wear plates welding