The uselife (service life) of a concrete mixer carbide blade versus a common blade (typically made of standard steel or low alloy steel) differs significantly due to material properties and wear resistance. Here’s a comparison:
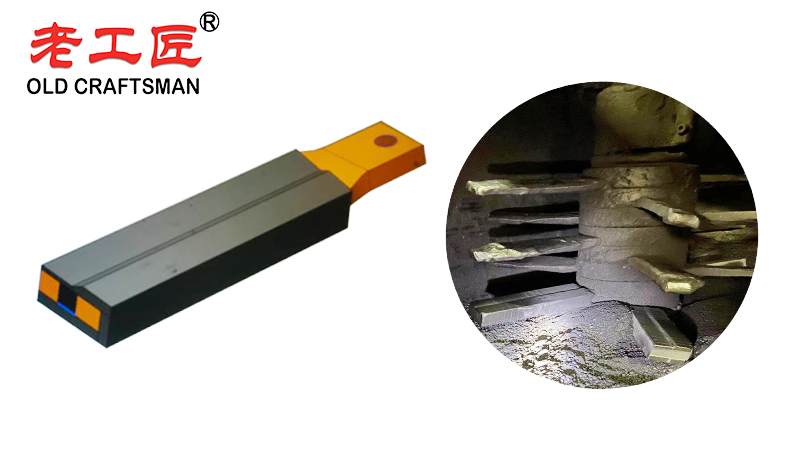

1. Carbide Blade (Tungsten Carbide-Tipped)
- Material: Made of high hardness tungsten carbide (WC) tips welded onto a steel body.
- Advantages:
- Extremely wear resistant (3-5x longer life than common steel blades).
- Better performance in abrasive concrete mixes (especially with sand, gravel, and additives).
- Resists corrosion from moisture and chemicals in concrete.
- Typical Lifespan:
- Dry Mix Applications: ~500-1,000 hours
- Wet Mix Applications: ~300-700 hours (depends on aggregate hardness)
- Best For: Heavy duty mixing, high abrasion environments, commercial/industrial use.
2. Common Steel Blade (Manganese Steel or Carbon Steel)
- Material: Made of standard or heat treated steel (e.g., 65Mn, high carbon steel).
- Advantages:
- Lower initial cost.
- Easier to sharpen or repair.
- Disadvantages:
- Wears out faster, especially in harsh mixes.
- Prone to rust and chemical erosion.
- Typical Lifespan:
- Dry Mix Applications: ~100-300 hours
- Wet Mix Applications: ~50-200 hours
- Best For: Light duty mixing, occasional use, budget projects.
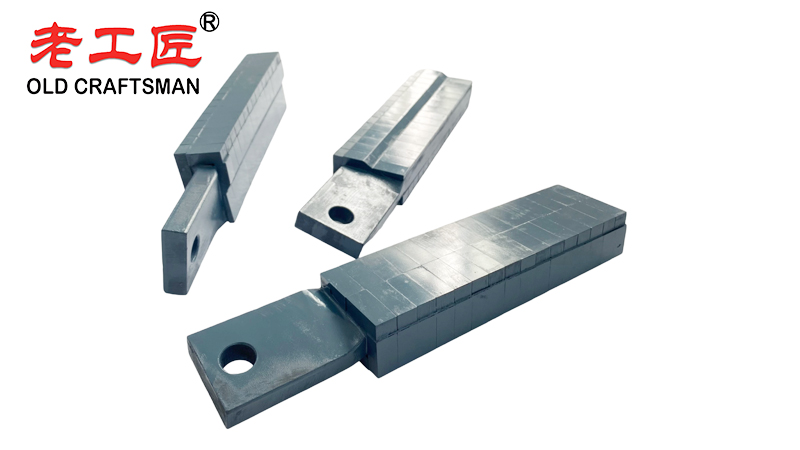

Key Factors Affecting Blade Life
- Mix Composition: Hard aggregates (quartz, granite) wear blades faster.
- Moisture Content: Wet concrete is less abrasive than dry mix but can cause corrosion.
- Mixer RPM: Higher speeds increase wear.
- Maintenance: Cleaning and proper storage extend blade life.
Conclusion
- Carbide blades last 3-5x longer than common steel blades but cost more upfront.
- Common blades are cheaper but require frequent replacement in heavy use.
For long-term cost efficiency in commercial mixing, carbide blades are superior. For occasional or light use, common steel may suffice.
High quality cutting tools are typically manufactured from tool steel or high carbon plain carbon steels, rather than mild steel, which contains only a low percentage of iron and carbon and lacks sufficient hardness for demanding applications. To achieve superior mechanical properties especially high yield strength and wear resistance the steel undergoes specific heat treatments. In the production of intensive mixers, the blades are often made from cold worked or cold rolled steel that is subsequently heated and subjected to controlled heat treatment processes (quenching and tempering) to obtain a fine grain structure and hardened steel condition. These heat treatments significantly improve hardness, toughness, and performance at both room temperature and elevated temperatures. The exact chemical composition of the steel, including alloying elements such as chromium, vanadium, or tungsten in tool steels, plays a critical role in determining the final properties and service life of the mixer blades and other high wear steel products.
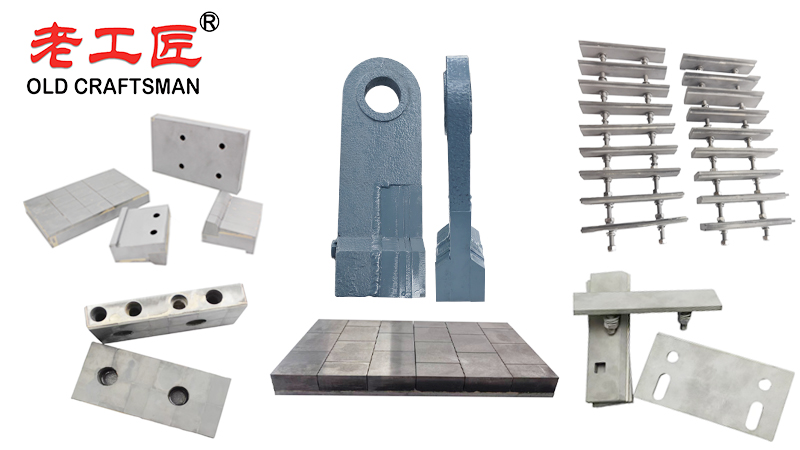
“Zhuzhou Old Craftsman Precision Alloy Co., Ltd. could make tungsten carbide wear parts and make your equipment use life is tens of times longer than before! We specialize in providing customized carbide wear products solutions to meet the demanding requirements of industries such as aerospace, automotive, mining, and precision machining.”
Belt scraper Brazing brazingprocess CARBDIE HAMMER carbide Carbide belt scraper carbidebrazing carbide hammer Crusher CRUSHER HAMMER Informational Internal stress metal mining Refractory Brick Mold Secondary belt cleaner scraper stresses VSI crusher wear plates welding
