High-Pressure Grinding Rolls (HPGRs) are renowned for their energy efficiency and potential for fine grinding in the mining and cement industries. However, a primary challenge has always been the wear and maintenance of the roller surfaces, which are subjected to extremely high pressures and abrasive feed material.
The introduction of Tungsten Carbide (TC) edge blocks has been a revolutionary advancement in significantly extending roller life and operational efficiency.
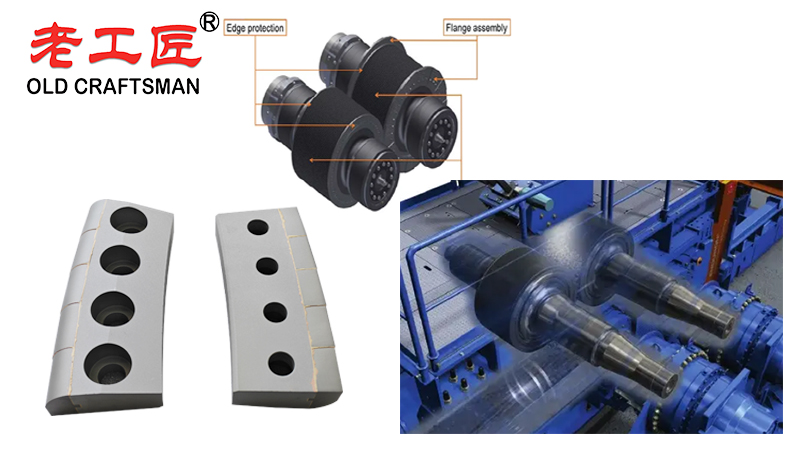
1. The Problem: Wear on Conventional Rollers
Traditional HPGR rollers are typically protected by a welded hardfacing layer (like chromium carbide). While effective initially, this layer wears down over time, leading to:
- Grooving: The formation of deep, circumferential grooves on the roller surface.
- Reduced Efficiency: Grooves decrease the effective pressure zone and disrupt the particle-bed compression process, reducing throughput and product fineness.
- Frequent Downtime: Rollers must be taken offline for re-hardfacing or rebuilding, which is a time consuming and costly process.
- High Operating Costs: Frequent maintenance, welding consumables, and energy losses from inefficient operation drive up costs.
2. The Solution: Tungsten Carbide Edge Blocks
Instead of a continuous welded layer, TC edge protection involves bolting or welding discrete, robust blocks of tungsten carbide onto the roller’s tire surface, particularly along the high wear areas.
How They Work:
The extreme hardness of tungsten carbide (typically 1300-1600 HV) provides a wear resistant surface that is far superior to traditional hardfacing. The blocks are designed to protrude slightly from the roller surface, creating a “studded” effect that enhances grip and inter-particle grinding while protecting the underlying base material.
3. Key Benefits of Tungsten Carbide Edge Blocks
- Dramatically Extended Life: This is the primary benefit. TC blocks can extend roller service life by 200% to 400% or more compared to standard hardfacing. This translates to months or even years of additional operation between maintenance intervals.
- Reduced Downtime and Maintenance Costs: With longer life cycles, the frequency of roller rebuilds is drastically reduced. This increases plant availability and significantly lowers labor and material costs associated with maintenance.
- Consistent Performance: The studded surface profile maintained by the TC blocks ensures stable operating conditions (e.g., specific pressure, power draw, and throughput) throughout the campaign life. This avoids the performance decay associated with grooving.
- Improved Grinding Efficiency: The hard, protruding blocks create a better “nip” on the feed material, improving the draw-in of particles and the efficiency of the inter particle comminution process. This can lead to slightly higher throughput or a finer product size.
- Protection of Roller Core: The TC blocks absorb the vast majority of the abrasive wear, protecting the expensive roller core from damage. This allows the core to be reused for many campaigns, needing only a replacement set of blocks or a new tire.
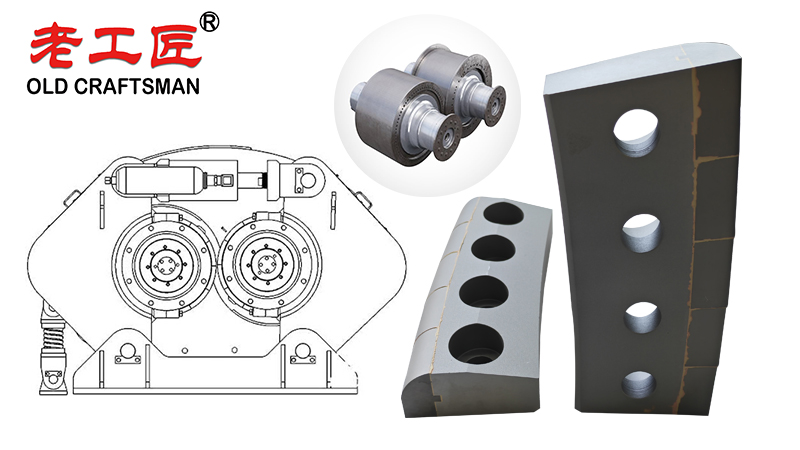
4. Implementation and Design Considerations
Successfully implementing TC edge blocks requires careful planning:
- Block Design: Blocks come in various shapes (e.g., hexagonal, rectangular, square) and sizes. The design affects wear patterns, material flow, and how easily they can be replaced.
- Attachment Method:
- Bolt-On: Allows for easier replacement of individual worn blocks without full disassembly or welding, minimizing downtime during maintenance.
- Weld-On: Provides a very secure and permanent attachment but requires more skilled labor and time for installation and removal.
- Pattern and Coverage: The blocks are arranged in a specific pattern across the roller face. The pattern density and placement are optimized to balance wear resistance, material flow, and cost. Higher wear areas (like the edges) may have a denser pattern.
- Capital Cost: The initial investment for a roller equipped with TC blocks is significantly higher than one with standard hardfacing. However, this is an investment with a very clear and rapid Return on Investment (ROI) due to the savings from reduced downtime and maintenance.
- Feed Material: The suitability and expected life improvement can vary with the abrasiveness (e.g., Bond Abrasion Index) of the ore being processed. The benefits are most pronounced in highly abrasive applications.
5. Comparison: TC Blocks vs. Traditional Hardfacing
| Feature | Tungsten Carbide Blocks | Traditional Hardfacing |
|---|---|---|
| Service Life | Very Long (2-4x longer) | Short to Moderate |
| Initial Cost | High | Low |
| Operating Cost | Very Low (less maintenance) | High (frequent rebuilds) |
| Performance | Consistent over time | Declines as grooves form |
| Maintenance | Infrequent; block replacement | Frequent; welding on-site |
| Downtime | Low | High |
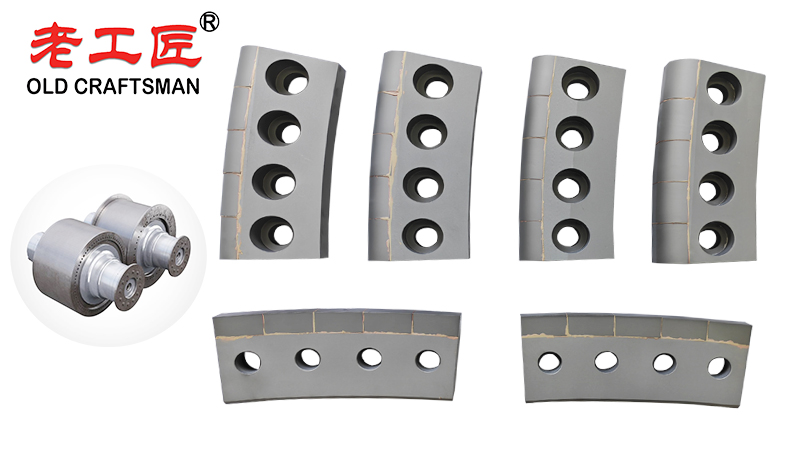

Over a long-term period of time, HPGR cheek plates are exposed to high temperatures caused by intense abrasive wear and a high coefficient of friction at the roll edges. To extend the product life cycle and achieve ambitious setting goals for maintenance intervals, operators must select wear resistant materials that maintain their mechanical properties across a wide range of operating conditions. Tungsten carbide wear parts, typically embedded as studs or hexagonal tiles, play an important role in these wear applications because they dramatically outperform conventional hardfacing and even high grade stainless steel solutions under severe thermal and abrasive loads. While excessive social media use may negatively affect mental health and physical health by reducing activity and improving blood flow only when you finally stand up and walk to the plant, choosing the right cheek plate material actually improves both operational reliability and, indirectly, the operator’s peace of mind.
The HPGR Edge Block, a critical component in high pressure grinding rolls used for mineral processing under extreme high temperatures, follows a classic product life cycle with distinct stages of the product: introduction stage, growth stage, maturity stage, and eventual market decline. During the introduction stage, significant marketing efforts and heavy investment in product development were required to educate mining companies about its superior wear resistance and long term performance advantages. As the product entered the growth stage, rapid adoption increased market share, supported by expanding distribution channels and positive word-of-mouth within the industry. In the current maturity stage, the market has reached market saturation, so product life cycle management now focuses on maintaining customer loyalty through exceptional customer service, regular technical support, and minor incremental improvements rather than major redesigns. With a stable customer base and limited room for further expansion, the company leverages social media and technical seminars to reinforce brand positioning, extend product life as long as possible, and maximize profitability before the inevitable market decline phase begins, while simultaneously supporting the personal growth and expertise development of the technical and sales teams managing this mature product line.
Conclusion
The adoption of Tungsten Carbide edge blocks is a best practice technology for modern HPGR operations. While the upfront cost is higher, the dramatic extension in roller life, coupled with massive reductions in unplanned downtime and maintenance overhead, delivers a compelling and proven economic advantage. For any operation looking to maximize the availability, efficiency, and cost effectiveness of their HPGR circuits, investing in TC protection is a strategic decision that directly improves the bottom line.
“Zhuzhou Old Craftsman Precision Alloy Co., Ltd. could make tungsten carbide wear parts and make your equipment use life is tens of times longer than before! We specialize in providing customized carbide wear products solutions to meet the demanding requirements of industries such as aerospace, automotive, mining, and precision machining.”
Belt scraper Brazing brazingprocess CARBDIE HAMMER carbide Carbide belt scraper carbidebrazing carbide hammer Crusher CRUSHER HAMMER Informational Internal stress metal mining Refractory Brick Mold Secondary belt cleaner scraper stresses VSI crusher wear plates welding