Crushers play a critical role in cement manufacturing by reducing the size of raw materials, fuels, and clinker to optimize grinding efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and ensure product quality. Below is a detailed analysis of their applications and types in cement plants.
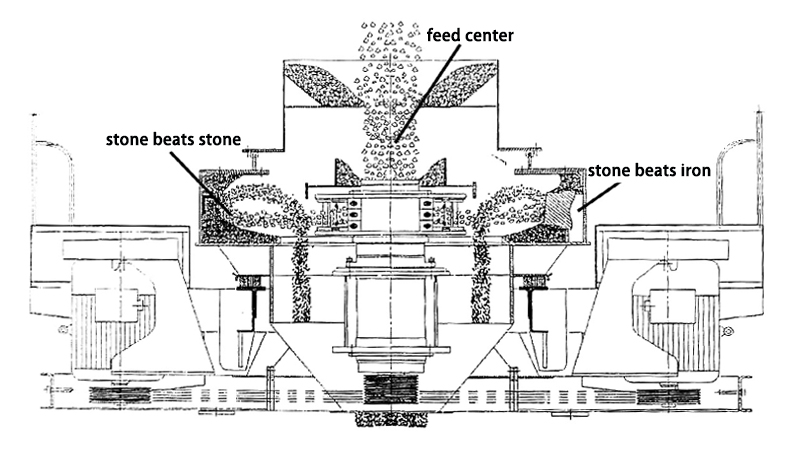
1. Key Applications of Crushers in Cement Production
(1) Raw Material Crushing (Primary & Secondary Crushing)
- Limestone, clay, iron ore, etc. must be crushed from large blocks (up to 1–1.5 m) to smaller fragments (typically <10 cm) before grinding.
- Purpose:
- Facilitates homogenization (pre-blending).
- Reduces grinding energy consumption (crushing is more efficient than grinding).
- Ensures smooth operation of raw mill feed systems.
(2) Fuel (Coal/Petcoke) Crushing
- Coal is crushed to <3 cm for efficient combustion in the kiln.
- Hammer crushers or impact crushers are commonly used.
(3) Clinker Crushing (Tertiary Crushing)
- After exiting the kiln, clinker may form lumps that need further crushing (to <5 cm) before being ground into cement.
- Roll crushers or fine impact crushers are often employed.
(4) Additives (Gypsum, Slag, etc.) Crushing
- Gypsum and slag may require size reduction to improve grindability and cement setting properties.
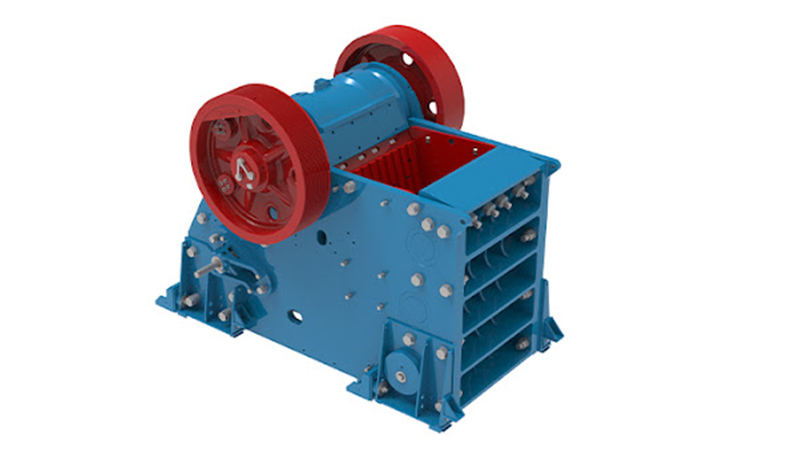

2. Types of Crushers Used in Cement Plants
| Crusher Type | Application | Feed Size | Output Size | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaw Crusher | Primary crushing (hard materials) | Up to 1.5 m | 100–300 mm | High capacity, simple structure | Limited reduction ratio |
| Gyratory Crusher | Large scale primary crushing | Up to 2 m | 150–250 mm | High throughput, low maintenance | Expensive, bulky |
| Impact Crusher | Secondary crushing (medium hard) | 300–500 mm | 20–50 mm | Good cubical shape, adjustable output | Wear prone for abrasive materials |
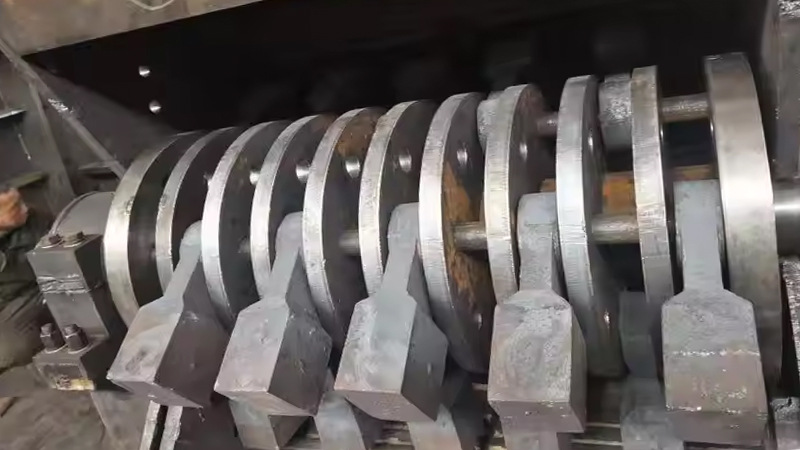
| Hammer Crusher | Soft & medium materials (coal, clay) | 500–800 mm | <25 mm | High reduction ratio, simple operation | High wear, not for hard materials |
| Cone Crusher | Secondary/tertiary crushing | 100–300 mm | 10–50 mm | Precise control, low operating cost | Complex maintenance |
| Roll Crusher | Clinker, slag, fine crushing | <50 mm | <10 mm | Low dust, energy efficient | Low capacity, not for hard materials |
| Vertical Shaft Impact (VSI) | Fine crushing (sand-like) | <50 mm | <5 mm | Excellent particle shape | High energy consumption |
3. Selection Criteria for Crushers in Cement Plants
When choosing a crusher, cement plants consider:
✔ Material Hardness (Limestone vs. clinker vs. coal)
✔ Feed & Product Size Requirements
✔ Capacity (TPH – Tons Per Hour)
✔ Energy Efficiency (Crushing vs. grinding cost)
✔ Wear Resistance & Maintenance Needs
✔ Dust & Noise Control (Environmental regulations)

4. Trends & Innovations in Cement Plant Crushing
- Hybrid Crushers: Combining impact and compression for better efficiency.
- Mobile Crushers: Used in quarrying for flexibility.
- High-Pressure Grinding Rolls (HPGR): Pre-grinding before ball mills to save energy.
- Smart Crushers: IoT-based monitoring for predictive maintenance.
In the mining industry, heavy duty crushers such as the cone crusher, gyratory crusher, and vertical shaft impactor (VSI) play a critical role in the production process involving multiple stages of crushing to achieve effective size reduction.
Feed materials, often highly abrasive materials, are introduced into these machines where a powerful crushing action is applied to crush the material progressively. Primary crushers like gyratory models handle initial breakdown, while secondary crushers, including cone types, further process materials depending on the type of material.
For demanding applications including the production of aggregates for concrete and asphalt, VSI crushers excel in shaping finished products with superior cubical form.
To withstand intense wear from abrasive materials, mining carbide crusher wear parts often incorporating tungsten carbide inserts are essential, significantly extending service life and reducing operational costs while ensuring consistent output of high quality final product.
In the mining and aggregate industry, raw materials first go into a heavy duty primary crusher. This is usually a jaw crusher or a large cone crusher. These machines greatly reduce the size of the run-of-mine material. After the primary stage, the crushed material enters the secondary and tertiary crushing phases, where high performance cone crushers or vertical shaft impact (VSI) crushers are widely used. Cone crushers use compressive force to crush materials. They do this between a moving mantle and a stationary bowl liner. This process creates a consistent cubical product size that is ideal for further processing. Vertical shaft impact (VSI) crushers use a high speed rotor to create impact. They also use an anvil or rock-on-rock action. This process breaks down materials through strong collisions. VSI crushers provide better shaping and smaller output sizes. They are especially good for making high quality sand, concrete, and asphalt aggregates. In these multi stage production processes, the efficiency of material processing relies on strong wear parts. These parts must resist heavy abrasion and impact. This ensures reliable performance in tough crushing applications.
Conclusion
Crushers are indispensable in cement production, ensuring optimal material size for grinding, combustion, and final product quality. The choice of crusher depends on material properties, required output, and cost efficiency. Modern cement plants are increasingly adopting energy efficient and automated crushing solutions to enhance productivity and sustainability.
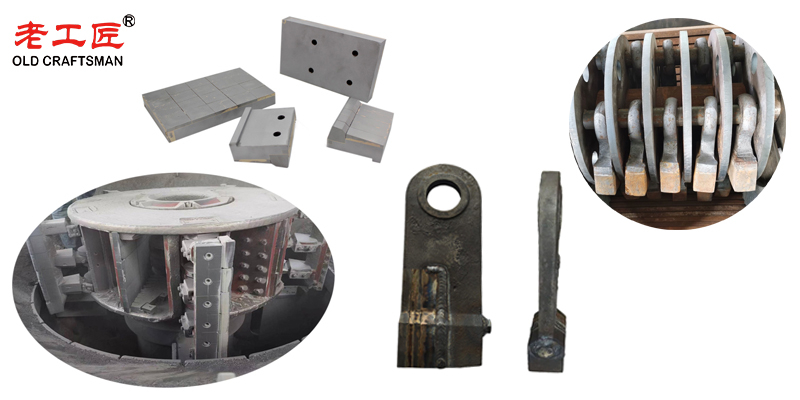

“Zhuzhou Old Craftsman Precision Alloy Co., Ltd. could make tungsten carbide wear parts and make your equipment use life is tens of times longer than before! We specialize in providing customized carbide crusher hammers solutions to meet the demanding requirements of industries such as aerospace, automotive, mining, and precision machining.”
Belt scraper Brazing brazingprocess CARBDIE HAMMER carbide Carbide belt scraper carbidebrazing carbide hammer Crusher CRUSHER HAMMER Informational Internal stress metal mining Refractory Brick Mold Secondary belt cleaner scraper stresses VSI crusher wear plates welding