Many people may not be very familiar with cemented carbide. As a professional cemented carbide manufacturer, Old Craftsman is here today to provide an introduction to the basic knowledge of tungsten carbide.
Tungsten carbide, often referred to as the “teeth of industry,” has a wide range of applications, including engineering, machinery, automotive, shipbuilding, optoelectronics, military, and more. The tungsten carbide industry consumes over half of the total tungsten consumption. We will introduce it from the perspectives of its definition, characteristics, classification, and applications.
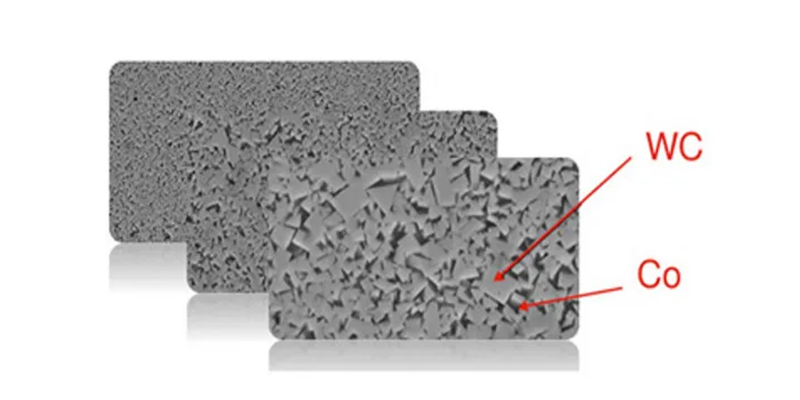
1. Definition
Tungsten carbide is an alloy made primarily from tungsten carbide powder (WC) as the main material, with metals such as cobalt, nickel, or molybdenum as binders. Its composition is similar to that of high density tungsten alloys, which use tungsten as the hard phase and metals like nickel, iron, or copper as the binding phase.
2. Characteristics
- High Hardness: Ranges from 86 to 93 HRA (equivalent to 69 to 81 HRC). Higher tungsten carbide content and finer grain size result in greater hardness under the same conditions.
- Excellent Wear Resistance: Tools made from this material last 5 to 80 times longer than high speed steel tools; molds made from it last 20 to 150 times longer than steel molds.
- Superior Heat Resistance: Hardness remains nearly unchanged at 500°C and stays high even at 1000°C.
- Strong Corrosion Resistance: Under normal conditions, it does not react with hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid.
- Good Toughness: Determined by the binding metal; higher binding phase content leads to greater bending strength.
- High Brittleness: Its inability to be machined makes it difficult to produce tools with complex shapes.
3. Classification
Based on the binder, tungsten carbide can be divided into the following categories:
- Tungsten Cobalt Alloys: Mainly composed of tungsten carbide and cobalt, used for tools, molds, and geological mining products.
- Tungsten Titanium Cobalt Alloys: Composed of tungsten carbide, titanium carbide, and cobalt.
- Tungsten Titanium Tantalum (Niobium) Alloys: Composed of tungsten carbide, titanium carbide, tantalum carbide (or niobium carbide), and cobalt.
Based on shape, they can be classified into spherical, rod shaped, and plate shaped forms. Non-standard products have unique shapes and require customization. Zhuzhou Old Craftsman Precision Alloy Co., Ltd. provides professional grade selection references.

4. Preparation
- Mixing: Raw materials are mixed in specific proportions.
- Wet Milling: Mixed with alcohol or other media and wet milled in a ball mill.
- Drying and Forming: After crushing, drying, and sieving, a forming agent like wax or glue is added.
- Pressing and Sintering: The mixture is granulated, pressed, and heated to produce the alloy product.
5. Applications
Tunsgten carbide is used to manufacture drills, cutting tools, rock drilling tools, mining tools, wear-resistant parts, cylinder liners, nozzles, motor rotors, and stators, among others.

Pure tungsten and cemented carbide are two key materials that resist wear. They are used in high performance industries, especially in extreme conditions. Pure tungsten possesses exceptional physical and mechanical properties, including the highest melting point of all metals (~3422 °C), very high density (~19.3 g/cm³), excellent strength at elevated temperature, and good corrosion resistance, making it ideal for specific applications such as radiation shielding, furnace components, and electrical contacts. Cemented carbide (typically tungsten carbide particles bonded with cobalt) combines the unique properties of hardness and toughness, offering outstanding wear resistance at both room temperature and elevated temperature, while maintaining reasonable fracture toughness. Cemented carbide is a popular choice for tough industrial uses. It is especially used in cutting tools, drill bits, and wear parts. This material is important in the oil and gas sector, mining, and metalworking industries. Its high hardness, strength, and resistance to wear are key for performance and tool life.
“Zhuzhou Old Craftsman Precision Alloy Co., Ltd. could make tungsten carbide wear parts and make your equipment use life is tens of times longer than before! We specialize in providing customized carbide wear products solutions to meet the demanding requirements of industries such as aerospace, automotive, mining, and precision machining.”
Belt scraper Brazing brazingprocess CARBDIE HAMMER carbide Carbide belt scraper carbidebrazing carbide hammer Crusher CRUSHER HAMMER Informational Internal stress metal mining Refractory Brick Mold Secondary belt cleaner scraper stresses VSI crusher wear plates welding